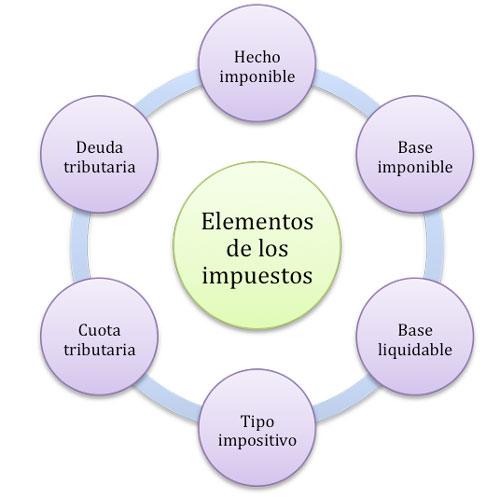
It is important that you learn about tax elements and its difference with the contributions since they are not the same even though the contributions are classified in taxes, but specifically …
What are taxes
the tax elements They can be understood if you first know that the taxes are taxes that do not require a consideration, that is, the taxes are payable to the State as part of a contribution with the treasury for the financing of the State’s public expenses, so that it can provide to the community a good port infrastructure, electricity, roads, benefits for work accidents, unemployment or disability etc.
In addition, taxes are regulated by a mandatory tax system regardless of their type.

Tax types
Laos taxes can be direct, indirect and progressive, for example:
Direct taxes
They are applicable periodically and individually to legal or natural persons according to their economic income and assets, such as wealth tax, income tax, inheritance tax, on the possession of cars or vehicles, to the use of the same and to the possession of animals, etc.
Direct taxes include product taxes, that is, those that are applicable to assets, heritage products and income, whose tax has to do with the nature of the assets and not the owner thereof.
They also include personal taxes applicable to wealth or income that belongs to legal or physical persons related to their ability to pay.
Existing taxes
VAT is also considered as an existing tax applied to the goods sold and according to that merchandise its percentage is variable, since while 18% is the burden of VAT tax in Spain, it is 15% in Mexico with the exception of the north. and the south and border strips where the VAT tax burden is 10%, 21% in Argentina variable according to the product, 12% in Ecuador, 10% in Paraguay, 19% in Chile and 12% in Guatemala.
Progressive taxes
As its name indicates, progressive taxes are those that to be calculated it is necessary to apply a rate or percentage that will grow according to how it increases based on. A practical example is income, the higher the income, the higher the percentage for the calculation.
Indirect taxes
They are applied to consumer goods and merchandise. The clearest example is VAT, or value added tax. It is a tax that has an impact on consumption and is also required in business activities, in the provision of services, transactions and professional activities.
Contribution elements
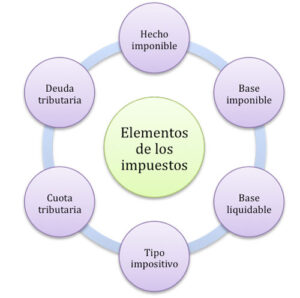 The elements of the contributions are five taxable event, taxpayer, tax base, fee and accrual.
The elements of the contributions are five taxable event, taxpayer, tax base, fee and accrual.
Taxable event
It is the element of the economic and legal tax that is established by law in order to apply the tax, which implies a tax obligation and payment of the tax.
Passive subject
The taxable person is the legal or natural person who is obliged to pay a tax obligation, must comply with these obligations to be considered as a taxpayer.
Tax base
The tax base is the total value on which a tax is calculated, for its calculation the tax base is multiplied by the percentage of a specific tax rate.
The fee
It is the tax rate is the final result after having applied the tax to the tax base.
Accrual
The accrual of the tax defines the taxable event carried out according to the law. Its principle derives from an accounting standard that indicates that every economic event or transaction is recorded when it occurs, regardless of the date of collection or payment.
Tax characteristics
Taxes must conform to certain characteristics such as:
- All taxes must be established in accordance with the law of the country.
- Taxes are an obligation of the taxpayer to the tax agent who is the creditor.
- All taxes must be calculated equitably and proportionally.
- Taxes correspond to both individuals and legal entities.
- These natural or legal persons must be considered as such as such according to what the law indicates.
- The collection of the tax must be applied to face public spending.
- Its application must be aimed at ensuring that tax revenues can meet public needs indirectly.
For example, taxes are collected by the state, then the state is responsible for producing thanks to the collection and that money is used to finance public services.
- However, it is also characterized by satisfying the needs directly such as those imposed on alcoholic beverages or cigarettes.
- When it comes to a special contribution, its origin as a tax obligation is enforceable when it functions as a special benefit for taxpayers.
- However, the special contribution is also characterized by the obligation to comply with what the law dictates.
- They are characterized by being compensatory to society in order to obtain homogeneous taxpayers.
- They must always be fair, since otherwise they would become abusive, which would lead to a recession in consumption and businesses would be paralyzed.
- They must also be equitable because if they are partially applied to only some consumable products it would affect sectors of production,
- Taxes should generate a redistribution of the collection in an equitable manner according to the income of the taxpayer in order to maintain social equality and not cause marked differences.
- However, in times of recession, taxes can increase their rate in order to consolidate the income of the public administration provided that this increase is applied in a balanced way, since if not applied in this way it would affect the final consumer and Business.
Then once redistributed it is an incentive for private investment, improvements can be made in public infrastructure, which means a better quality of life for taxpayers including an increase in wages.