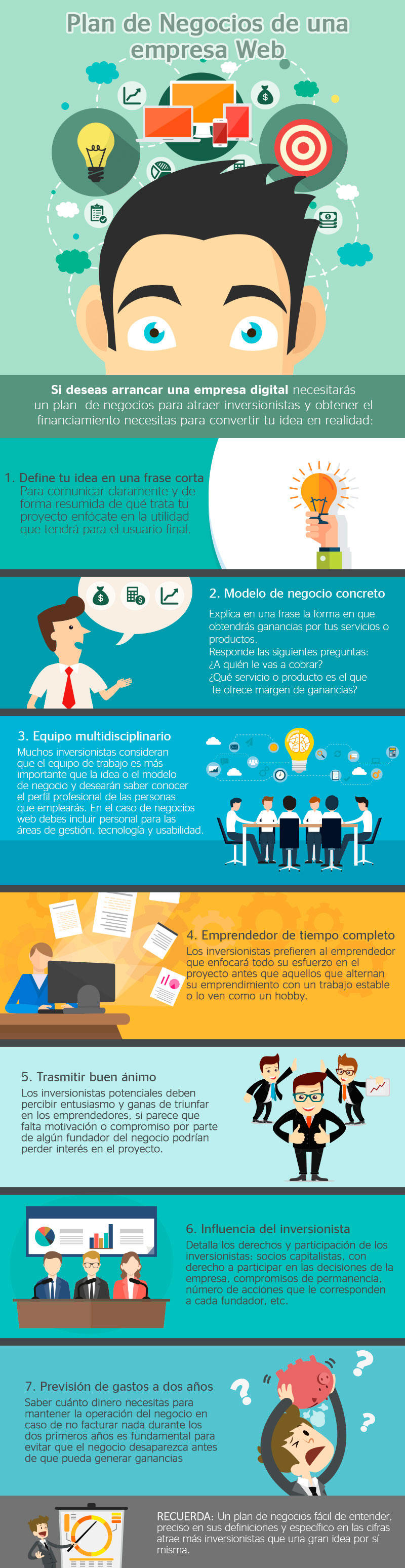
Your business plan is the foundation of your business. Learn how to write a business plan quickly and efficiently with a business plan template.
Business plans help you run your business
A good business plan guides you through each stage of building and managing your business. You will use your business plan as a roadmap to structure, execute, and grow your new business. It is a way of thinking through the key elements of your business.
 Business plans can help you raise funds or attract new business partners. Investors want to feel confident that they will see a return on their investment. Your business plan is the tool you will use to convince people that working with you or investing in your company is a smart choice.
Business plans can help you raise funds or attract new business partners. Investors want to feel confident that they will see a return on their investment. Your business plan is the tool you will use to convince people that working with you or investing in your company is a smart choice.
Choose a business plan format that works for you.
There is no right or wrong way to write a business plan. The important thing is that your plan meets your needs.
Most business plans fall into two common categories: traditional or from Lean Startup.
Traditional business plans are more common, use a standard structure, and encourage you to go into detail in each section. They tend to require more work up front and can be dozens of pages.
Lean startup business plans are less common but still use a standard structure. They focus on summarizing only the most important points of the key elements of your plan. They can take as little as an hour to make and are typically a single page.
Traditional business plan
This type of plan is very detailed, takes longer to write, and is comprehensive. Lenders and investors commonly request this plan.
Lean Startup Plan
This type of plan is high-level, quick to write, and contains only key elements. Some lenders and investors may request more information.
Traditional business plan format
 You may prefer a traditional business plan format if you are very detail-oriented, want a comprehensive plan, or want to apply for financing from traditional sources.
You may prefer a traditional business plan format if you are very detail-oriented, want a comprehensive plan, or want to apply for financing from traditional sources.
When you write your business plan, you don’t have to stick to the exact outline of the business plan. Instead, use the sections that make the most sense for your business and your needs. Traditional business plans use some combination of these nine sections.
Executive Summary
Briefly tell your reader what your business is and why it will be successful. Include your mission statement, your product or service, and basic information about your leadership team, employees, and location. You should also include high-level financial information and growth plans if you plan to apply for financing.
Company description
Use your business description to provide detailed information about your business. Go into detail about the problems your business solves. Be specific and make a list of the consumers, organization, or businesses that your business plans to serve.
Explain the competitive advantages that will make your business a success. Are there experts on your team? Have you found the perfect location for your store? Your business description is the place to show off your strengths.
Market analysis
You will need a good understanding of the prospects for your industry and the target market. Competitive research will show you what other companies are doing and what their strengths are. In your market research, look for trends and topics. What do successful competitors do? Why does it work? Could you do it better? Now is the time to answer these questions.
Organization and management
Tell your reader how your business will be structured and who will run it.
Describe the legal structure of your business. Indicate if you have or intend to incorporate your business as a C or S corporation, form a general or limited partnership, or if you are a sole proprietor or LLC.
Use an org chart to establish who is in charge of what in your company. Show how each person’s unique experience will contribute to the success of your business. Consider including resumes and resumes of key members of your team.
Service or product line
Describe what you sell or what service you offer. Explain how it benefits your customers and what the product life cycle looks like. Share your plans for intellectual property, such as patent or copyright applications. If you are doing market research and competitive analysis for your service or product, explain it in detail.
Marketing and sales
There is no one way to approach a marketing strategy. Your strategy must evolve and change to suit your unique needs.
Your goal in this section is to describe how to attract and retain customers. It will also describe how a sale will be made. You will refer to this section later when making financial projections, so be sure to fully describe your marketing and sales strategies.
Financing request
If you are applying for financing, this is where you will describe your financing requirements. Your goal is to clearly explain how much money you will need in the next five years and what you will use it for.
Specify whether you want debt or equity, the terms you want to apply, and the time period your request will cover. Provide a detailed description of how you will use your funds. Specify whether you need funds to buy equipment or materials, pay salaries, or cover specific bills until income increases. Always include a description of your future strategic financial plans, such as paying off debt or selling your business.
Financial projections
Supplement your financing request with financial projections. Your goal is to convince the reader that your business is stable and will be financially successful.
If your business is already established, include income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements for the past three to five years. If you have other collateral that you could put against a loan, be sure to list it now.
Provide a forward-looking financial outlook for the next five years. Include projected income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and capital expenditure budgets. For the first year, be even more specific and use quarterly – or even monthly projections. Be sure to clearly explain your projections and match them with your funding requests.
This is a great place to use charts and graphs to tell the financial story of your business.
Appendix
Use your appendix to provide supporting documents or other specially requested materials. Common items to include are credit histories, resumes, product photos, letters of reference, licenses, permits or patents, legal documents, permits, and other contracts.
Examples of business plans
If you want to know how to go about writing your business plan, read these sample business plans written by fictitious business owners. Robert owns a consulting firm (Sample Business Plan Firm), and Andres owns a toy company.

Lean Startup format
You may prefer a format of Lean Startup Format if you want to explain or start your business quickly, if your business is relatively simple, or if you plan to change and refine your business plan regularly.
The formats of Lean Startup they are charts that use only a handful of elements to describe your company’s value proposition, infrastructure, customers, and finances. They are useful for visualizing fundamental facts and balances about your business.
There are many versions of templates Lean Startup Format, but one of the oldest and best known is the Business Model Canvas, developed by Alex Osterwalder. You can search the web to find free templates of the business model canvas, or other versions, to build your business plan.
We will discuss the nine components of the Business Model Canvas version here.
Key alliances
Consider the other businesses or services you will be working with to run your business. Think of similar suppliers, manufacturers, subcontractors, and strategic partners.
Main activities
Make a list of the ways your business will gain a competitive advantage. Highlight things like selling directly to consumers or using technology to take advantage of the sharing economy.
Key resources
Make a list of any resources that you can leverage to create value for your customer. Your most important assets could include personnel, capital, or intellectual property. Be sure to take advantage of business resources that may be available to HUBZone women, veterans, Native Americans, and businesses.
Value proposal
Make a clear and compelling statement about the unique value your company brings to the market.
Relationships with customers
Describe how customers will interact with your business. Is it automated or personal? In person or online? Think about the customer experience from start to finish.
Customer Segments
Be specific when naming your target market. Your business will not be for everyone, so it is important to have a clear idea of who your business will serve.
Channels
Make a list of the most important ways you will talk to your customers. Most companies use a mix of channels and optimize them over time.
Cost structure
Will your company focus on reducing costs or maximizing value? Define your strategy, then list the most significant costs you will face in following it.
Income stream
Explain how your company will actually make money. Some examples are direct sales, membership fees, and the sale of ad space. If your business has multiple sources of income, please list them all.
Lean Business Plan Example
Before writing your business plan, read this sample business plan written by fictitious business owner Andrew, who owns a toy company.
Business plan tool
The SBA Business Plan Tool provides you with a step-by-step guide to creating your business plan. You can save your plan online and update it at any time, or download it as a PDF file. You must re-register as a user to use this tool, you can do it for free from the next link.

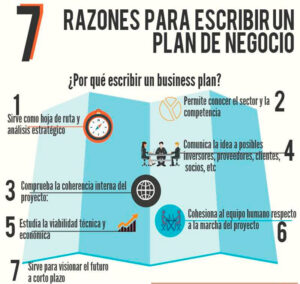
Infographic: Business plan of a company