The recent discovery of monkeypox in Florida has created concern and interest. Although relatively rare, we need to be vigilant about understanding the implications and potential impact of this disease. Monkeypox is a viral illness that is sometimes confused with smallpox due to clinical similarities. However, monkeypox is less severe than its relative, smallpox. Nevertheless, it can still be dangerous, and we need to be aware of its symptoms, treatment, and prevention measures.
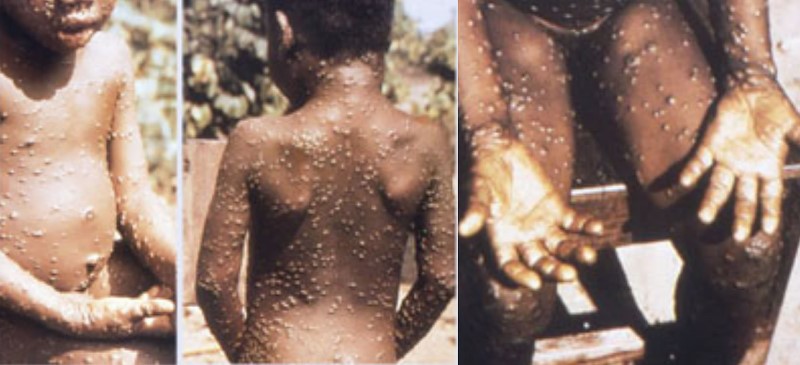
Monkeypox symptoms are similar to other viral illnesses, such as fever, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue. The virus can also cause a rash, similar to smallpox, but less severe. A distinguishing feature is the presence of pustules or bumps that can cover the entire body. Understanding these symptoms can help us recognize and diagnose monkeypox cases early.
The discovery of monkeypox in Florida raises concerns about an outbreak as the virus can be transmitted from animals to humans. Direct contact with infected animals or animal products, such as meat and milk, is a primary mode of transmission. Therefore, prevention measures, such as avoiding contact with infected animals, proper handling of animal products, vaccination, and isolation are crucial. Overall, we need to monitor the situation carefully and take appropriate measures to prevent the spread of this disease.
Responding to Section 2: Monkeypox Symptoms
Monkeypox is a rare viral disease that is similar to human smallpox. As the name suggests, it is commonly found in monkeys and other primates, with occasional transmission to humans. It has been reported in some parts of the world, including Africa and recently in the United States.
The symptoms of monkeypox include fever, headache, muscle aches, backache, swollen lymph nodes, chills, and exhaustion. After a few days, a rash appears that progresses to raised bumps filled with fluid that eventually become pustules. These bumps will spread over the face, trunk, and limbs, accompanied by intense itching.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms after a visit to a monkeypox-infected area. Although there is no specific treatment for monkeypox, health professionals can provide supportive care to manage the symptoms.
Preventing monkeypox is also essential, and this can be done by avoiding contact with infected animals, especially monkeys, squirrels, and other rodents found in the same area. Additionally, a vaccine that is effective for smallpox also provides immunity against monkeypox. So, individuals who have been vaccinated for smallpox are less likely to be infected with monkeypox.
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of monkeypox can help to curb its spread and keep individuals safe. It is also essential to seek medical attention promptly for proper management of the disease.
Monkeypox Outbreak
The monkeypox outbreak is a serious concern as it can lead to severe illness in humans. It is important to stay informed about the outbreak and its spread. Some common measures to prevent the outbreak include avoiding contact with infected animals, washing hands regularly, and avoiding crowded areas. In case of any symptoms or suspected exposure, seek medical attention immediately. It is crucial to stay aware of the latest news and updates about the outbreak to take necessary precautions.
Monkeypox Transmission: How the Virus Spreads
Monkeypox is a rare but serious viral disease that can be transmitted from animals to humans, as well as between humans. While it is a member of the same family of viruses as smallpox, monkeypox is not as deadly. However, the disease is highly contagious and can cause severe illness, so it is important to understand how it spreads.
Here are the ways in which monkeypox can be transmitted:
To prevent the transmission of monkeypox, it is important to avoid contact with infected animals and to practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands regularly and covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing. Vaccination and treatment options are also available, so if you suspect you have been exposed to monkeypox, seek medical attention immediately.
Monkeypox Treatment
Monkeypox is a viral disease that causes fever, headache, muscle aches and a rash. There is no specific treatment for monkeypox, but the symptoms can be managed. The primary focus of treatment is reducing the severity of symptoms and providing supportive care. This typically includes taking acetaminophen or ibuprofen to reduce fever and relieve pain, drinking plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration, and keeping the rash clean and covered. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to ensure adequate hydration, prevent complications, and provide supportive care.
Antiviral medications may also be used to treat monkeypox, but their effectiveness is not yet well established. Currently, there is no approved vaccine for monkeypox in humans, although a vaccine is available for use in animals.
Preventing the spread of monkeypox is important, and people who have symptoms of the disease should seek medical care right away. To reduce the risk of monkeypox, it is important to avoid contact with infected animals, practice good hygiene, and follow recommended guidelines for handling and preparing food. With proper care and treatment, most people with monkeypox make a full recovery within a few weeks. Remember to always seek medical attention from a trained professional if you suspect you may have monkeypox.
Monkeypox Vaccine
Monkeypox is a rare viral disease that can cause a high fever, rash, and other symptoms. It is similar to smallpox, but less severe. While monkeypox is not typically fatal, it can be dangerous for those with weakened immune systems. The good news is that there is a monkeypox vaccine available that can help prevent the disease.
The monkeypox vaccine is made from a live virus that is related to the monkeypox virus. It is similar to the smallpox vaccine, which was used to eradicate smallpox from the world. The vaccine is given to people who are at high risk of getting monkeypox, such as those who work with animals or in areas where monkeypox is known to be present.
The monkeypox vaccine is highly effective at preventing monkeypox. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the vaccine can reduce the risk of getting the disease by up to 95%. The vaccine is given in two doses, with the second dose given four weeks after the first.
It is important to note that the monkeypox vaccine is not routinely recommended for the general public, as monkeypox is a rare disease. However, if you are at high risk of exposure to the virus, such as if you work with animals, you should talk to your healthcare provider about getting vaccinated.
In summary, the monkeypox vaccine is a highly effective way to prevent monkeypox, and those at high risk of exposure to the virus should consider getting vaccinated. If you have any concerns about monkeypox or the vaccine, be sure to talk to your healthcare provider.
Monkeypox virus
Monkeypox virus is the cause of the monkeypox disease that affects humans and some animals, particularly monkeys. The virus belongs to the same family as the smallpox virus and is closely related to it. Monkeypox virus is transmitted from animals to humans through contact with the infected animal’s bodily fluids or through a bite or scratch from the animal. The virus can also spread from person to person through respiratory droplets or contact with contaminated objects.
The symptoms of monkeypox virus include fever, headache, muscle aches, and a rash that develops into pustules. The disease can be severe, but it is usually self-limiting and resolves within two to three weeks. There is no specific treatment for monkeypox virus, but supportive care can help manage symptoms.
Preventing monkeypox virus infection involves avoiding contact with infected animals and practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding touching the face. A vaccine for monkeypox virus exists, but it is not widely available.
Awareness of monkeypox virus and its transmission is crucial to prevent the spread of the disease. Regular updates on monkeypox news and the number of monkeypox cases can help identify outbreaks and prevent further spread. Early diagnosis of monkeypox virus is essential, and healthcare providers should be aware of the symptoms of monkeypox and how to identify the disease. Overall, preventing monkeypox virus requires a combination of public health measures and individual responsibility.
Monkeypox in Humans
Monkeypox is a viral disease that can affect humans. It is caused by the monkeypox virus and is similar to smallpox, but much less severe. The virus is typically found in animals in Central and West Africa, but cases of monkeypox in humans have been reported in other parts of the world, including Florida.
Monkeypox in humans can cause fever, headache, muscle aches, and a rash. The rash usually starts on the face and then spreads to other parts of the body. The disease can also cause swelling of the lymph nodes, which can be painful.
Monkeypox is spread to humans through contact with infected animals or people. In some cases, the disease can be transmitted from person to person through respiratory droplets or contact with bodily fluids.
There is no specific treatment for monkeypox, but antiviral medications may be used to help manage symptoms. A vaccine for monkeypox is also available, but it is only recommended for people who are at high risk of exposure, such as laboratory workers and healthcare professionals.
To prevent monkeypox, it is important to avoid contact with infected animals and people. This includes avoiding contact with wild animals in areas where monkeypox is known to occur, and practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and avoiding touching your face.
If you think you may have monkeypox, it is important to seek medical attention right away. A healthcare provider can diagnose the disease based on symptoms and other factors, such as recent travel or exposure to infected animals.
Old-Fashioned Aerial Depictions of My Habitat
Section 9 of the table of contents offers a variety of ways to describe vintage aerial photos of a specific residence. The title, “Old-Fashioned Aerial Depictions of My Habitat” is one such description. These types of photos offer a glimpse into the past, allowing us to see how a particular area has changed over time. They can also hold sentimental value for those who have a personal connection to the location. Whether referred to as vintage, historical, antique, retro, classic, nostalgic, timeless, archival, traditional, aged, ancient, or outdated, aerial photos of a dwelling can provide valuable information and perspective.
Monkeypox Prevention: Key Strategies for Staying Safe
Prevention is crucial when it comes to monkeypox, as there is currently no cure for the viral infection. The good news is that there are several steps you can take to protect yourself from contracting the virus.
1. Avoid contact with animals – Monkeypox is primarily spread through direct contact with infected animals, such as rodents, monkeys, and other primates. Avoid handling these animals or their bodily fluids, and do not consume bushmeat.
2. Practice good hygiene – Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after coming into contact with animals or their environments. Avoid touching your face, particularly your eyes, nose, and mouth.
3. Wear protective clothing – If you must handle animals or their bodily fluids, wear protective clothing such as gloves, masks, and gowns.
4. Stay away from affected areas – If there is an outbreak of monkeypox in a certain area, avoid traveling there if possible. If you must go, take extra precautions to protect yourself.
5. Get vaccinated – There is currently a vaccine available for monkeypox, which can provide protection for up to 10 years. If you are at high risk of exposure, such as laboratory workers or healthcare providers, consider getting vaccinated.
By following these key strategies, you can reduce your risk of contracting monkeypox. Stay up-to-date on the latest news and information about monkeypox prevention and outbreaks to ensure you are taking the necessary precautions.
Responding to Section 11: Aged Aerial Graphics of My Place of Residence
Section 11 of the table of contents refers to aged aerial graphics of one’s place of residence. It is fascinating to see historical aerial pictures of our abode and how it has changed over time. Vintage aerial photos can offer a unique perspective on our homes and neighborhoods and can be a valuable resource for historical and architectural research.
Through these aged aerial graphics, we can see the development and growth of our surroundings, witness changes that have occurred over time, and appreciate the historical context of our dwelling place. By analyzing the changes in our communities, we can learn about the cultural, social, and economic history of the region.
Overall, aged aerial graphics of our place of residence provide us with a glimpse into the past and add to our understanding of our community’s evolution. They are a fascinating reminder of the rich history that exists in our neighborhoods and can help us appreciate the unique character and identity of our homes and surrounding environment.
Response to Section 12: Monkeypox Cases
Monkeypox cases refer to the recorded incidents of individuals who have contracted the monkeypox virus. As a highly infectious and deadly disease, monkeypox cases have been a concern for both health officials and the general public alike. The number of monkeypox cases varies depending on the region and year, with some areas experiencing numerous outbreaks while others remain relatively untouched.
It is essential to note that while monkeypox cases tend to occur in remote areas of Central and West Africa, recent outbreaks in the United States and other countries have raised concerns. These cases highlight the need for proper diagnosis, treatment, and prevention measures to control the spread of the virus.
In conclusion, monitoring monkeypox cases and prioritizing interventions such as vaccination and infection control remain crucial in combating this disease’s impact. Strong public health measures and increased awareness can help prevent monkeypox cases and save lives.
Response to Section 12: Ancient aerial illustrations of my homestead
Looking at ancient aerial illustrations of your homestead can provide an invaluable insight into the history of your property. These images can help you understand the land’s original layout, as well as any changes that have occurred over time. By examining ancient aerial illustrations, you might discover traces of previous buildings or land use which could add interesting details to your property’s history. Furthermore, these illustrations can provide an interesting perspective on the natural environment surrounding your homestead, and how it has evolved over time. Analysing such ancient aerial illustrations can be a fascinating and rewarding experience for homeowners who are interested in uncovering the stories of their historic properties.